Silicon Valley Bank Crisis
Silicon Valley Banks ($SIVB) a bank which was a powerhouse for almost all venture capitalist and startup based fund had its Lehman Brothers moment in the past days. A $80 Billion loss of precious investor’s money was seen as the company announced to cease all of its operations which created a havoc among the biggest financial institutions of the world. The effects of an American Bank failing are far wide than any other Financial Catastrophe. Silicon Valley Bank held more than $175 Billion USD in deposits out of which only 2.7% of them were insured. According to the laws of Finance in the United States, FDIC (Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation) is an independent agency which insures depositors money upto $250,000. Any amount above 250k stands as uninsured money. Considering and keeping in mind that Silicon Valley Bank held mostly fund from Venture Capitalist and Startups, The 250 grands were nothing when compared to the funds held by these kind of accounts would be worth Billions and Billions of dollars. The crisis was contained in a kind of manner but the stake was the investors money and the depositors money was safe guarded.
What caused this havoc?
On Friday, 10th of March, Silicon Valley bank announced that the bank is shutting all its operations. Silicon Valley Bank had plans of raising around USD 21 Billion from investors to pay out depositors which caused a loss of $2 billion. Investors took this as a distress call and panicked to sell shares which caused the share falling down as much as 60% which in-turn caused a USD 80 Billion wipeout from just the drop in stock price of Silicon Valley Bank. The sudden distress call also caused the other banks like JP Morgan, etc to drop significantly. When considering other banks the market capitalisation loss would be upward of some 500–700 Billion USD.
So coming back to the story of what caused this kind of situation, Silicon Valley Bank had bought many billion dollars worth of bonds. A bank performs in a way where the bank keeps some amount of money as cash for any one who wants to take out money and other are invested in long term bonds or equities. The bank earns from long term equities, The loans also yield some amount of money as interest and the banks pays a lesser interest rate to the depositors. The difference of this interest rate is the way the bank earns interest this is known as the the Net Interest Income (NII).
In the wake of mass layoffs, There’s a startup funding freeze in the market. The federal reserve is a body which kept on increasing interest rate to curb inflation. The issue happened when there were no new funding rounds of companies so the companies started debiting the money present in the account. Soon the depositors corpus fund was down to zero and suddenly there was a negative cashflow which caused the bank to dilute some assets. This didn’t yield any result also. Hence as a last resort the company thought of raising funds (upto $21 Billion) to give back depositors money. The bank was successful on raising the capital but took a loss of $2 Billion. This was the ultimatum which caused the major meltdown.
When dealing in marketing and stuff, the cost to acquire a customer is called the Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC). When dealing with banking, the cost for acquiring a customer (or their deposit) is known as the Deposit Acquisition cost (DAC). As fundings stopped, The deposit acquisition cost shoot up which caused on more cash burn problem. The series of events unfolded in such a preposterous manner which caused a panic with investors and they sent the share tumbling upto more than 60% intraday and 96% from 52-week highs.
The Exposure
Silicon Valley Bank is the only second major US bank to fail just behind Washington mutual which failed during the crisis of 2008. The major panic was caused because of major tech companies had heavy deposits and exposure in the bank. The public announcement from Circle on USD 3.3 Billion exposure with Silicon Valley Bank caused major havoc. The KBW Nasdaq Regional Banking Index had dropped around 6.4% as this created an atmosphere with major other banks as well. Under a plan released on Wednesday, SVB was looking to sell 1.25 Billion USD worth of shares with an option of $500 million of convertibles. The fundraising plan came to a standstill as no companies (except General Atlantic) were ready to bail it out. Hence out of no options on Friday, SVB made official the censure of its operations.
The whole thought of stories unfolding didn’t prove any wrong doing or some scam kind of situation but it was again a big company trapping because of highly leveraged position. The leverage at the point was so high that the sudden buyout was raising funds and taking a loss on them. The bank very well knew that they might take a standstill as the deposits growth was in single digits and for the coming quarter it would be in negative. Hence without any sort of deposits there was possibly very less growth and the DAC was also rising.
A complete list of companies having exposure in Silicon Valley Bank is available below
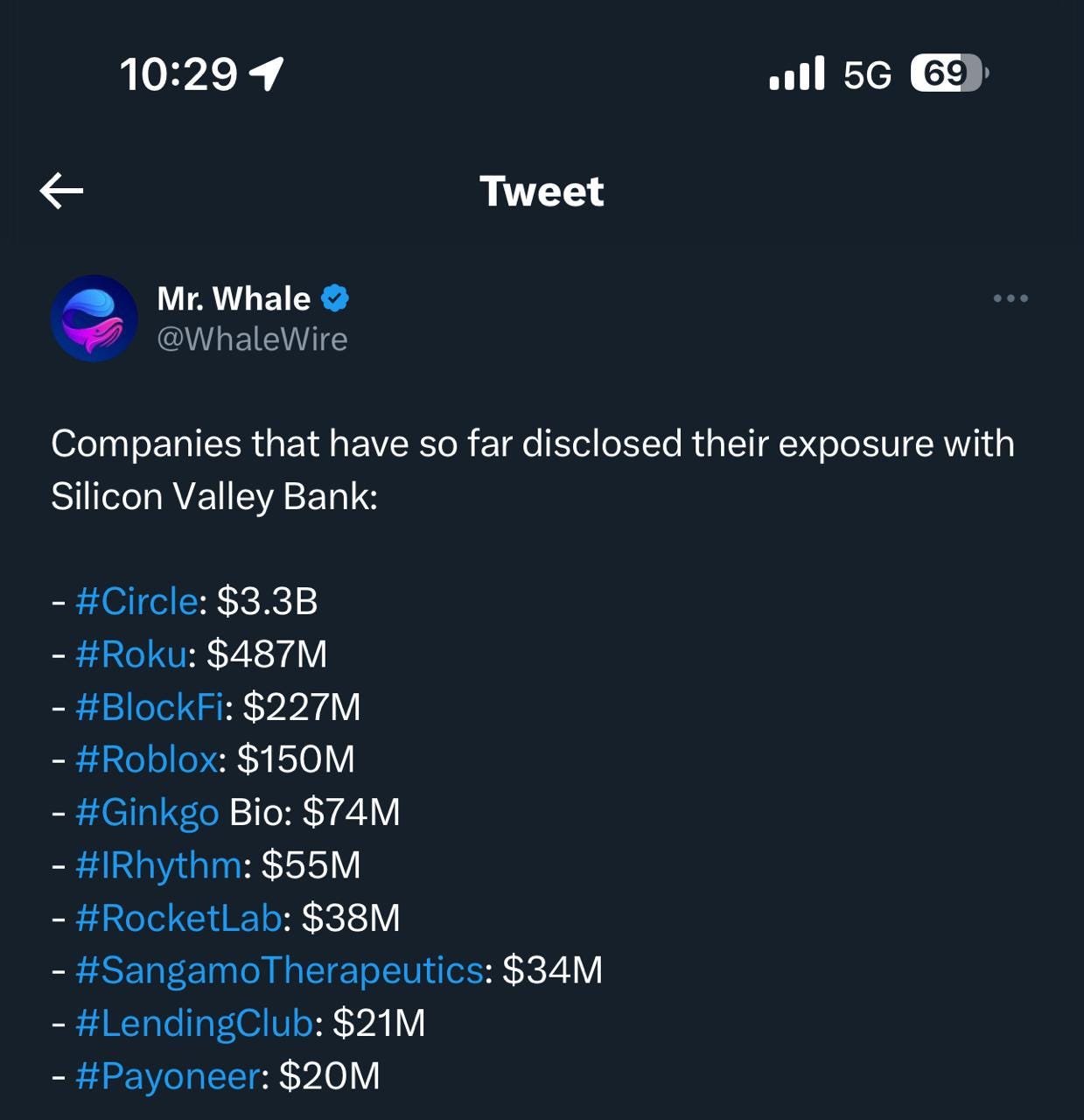
A complete list of exposed of all banks and their exposure is available below which shows that only 2.7% of bank deposits are issued by FDIC.

What’s Next
After unfolding of the event, Popular investor and banker Bill Ackman tweeted that the congress should bail out the bank as this implies to a bigger financial implication and can have a chain reaction of failed banks and can create jitters in the global financial system. To protect the world from these financial jitters, A congress bailout or another big financial institution buying it was the only way out. On Sunday, Treasure secretary Janet Yellen announced that they won’t bailout Silicon Valley Bank like they did in 2008. This waived of little hope of a congress bailout. A company based takeover is the only way out but looking at current situation and the rigid financials of the bank it’s most likely that neither of the financial player will put a hand in the same (Do check Sudden Developments).
To be clear, a bailout should be designed to protect @SVB_Financial depositors, not equity holders or management. We should not reward poor risk management or protect shareholders from risks they knowingly assumed.
— Bill Ackman (@BillAckman) March 10, 2023
After the collapse of such a big banks led to another big bank failure as regulators closed crypto-focused bank ‘Signature Bank’ citing systemic risk. Signature Bank had given heavy loans to crypto-based firms due to which this lender had to close their doors.
Deposits at both banks failed post Friday but late Sunday night an official memorandum was brought forward which stated that depositors can have access to their money but an official roadmap will be developed for the proper handling of both the failed banks. The US futures market cheered this decision which protects the depositors money and kept its safe from all the financial wrong doings happening at the bank. The federal reserve stepped in with a separate facility called as Bank Term Funding Programs that will provide loans upto one year for organisations affected by this kind crisis. Those using this facility will have to pledge high quality collaterals to avail loans from the treasury. Depositors will have full access to the money starting from Monday (13th of March,2023). The Treasury Department is providing up to $25 billion from its Exchange Stabilisation Fund as a backstop for any potential losses from the funding program.
Hence for time being it looks like the Silicon Valley Bank crisis is under control but what happens in the coming weeks will be worth seeing.
Sudden Developments
There have been some sudden major developments in this Silicon Valley Bank Story. Starting off with Silicon Valley Bank’s UK branch got acquired by HSBC for a mere token of just one British pound. SIVB’s total loans in the UK arms stand at 5.5 Billion GBP and have deposits of around 6.7 Billion GBP. A small amount to process for a bank like HSBC but an institution ready to take this challenge was a role forward. Another major development was the failing of another US lender by the name of First Republic Bank, This news got ignited when the stock was down around 60% in premarket hours. Dow Jones IA lost all its gains and traded in the negative side. Also when writing this, A NYSE broadcast says that multiple US banks have halted in trade (Image provided below). At open of today US markets (13th of March), Banking stocks in US have taken a major hit some are halved while some are down more than 65%. An image of the same has been seen below.
Conclusion
In the wake of this crisis it’s very evident that having a very highly leveraged position when dealing in banking can be very troublesome. We should also understand that banking is very deep rooted process, No one knows who is how exposed to a Banking collapse. Hence having a very staunch, guided and diversified approach is very necessary. Banks perform in a very systematic manner and they need to work according to a set of approach which wasn’t the case in these banks
Thanks.